人類基因序列十分複雜,其中超過90%屬於「非編碼區域」,此非編碼區若產生變異可能影響基因調控,導致疾病發生,因此基因調控機制也成為許多科學家的研究重點。台大生物產業機電工程學系教授陳倩瑜的研究團隊開發出一套深度學習模型,能準確預測致病變異,協助精準診斷。
生機系表示,非編碼區域存在著許多基因的調控訊息,像是增強子、啟動子和轉錄因子結合位點,都是坐落於基因的非編碼區中,並互相影響交織成一個調控網路,若是在非編碼區中產生了變異,可能會影響到基因的調控,導致疾病的產生,所以需要對基因的調控做深入研究,來了解基因變異如何造成疾病的產生。
而陳倩瑜教授的研究團隊目前已實作一套能夠預測K562細胞株中轉錄因子結合位點的深度學習模型,該模型利用「卷積神經網路」(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)的特點來達成預測,CNN是一種模仿人類大腦認知方式的演算法,這個深度學習模型利用CNN在圖像學習上的概念及優點,將一維的序列轉化為類似於圖像的二維的陣列來做學習,可達到平均83.3%的預測準確率。因此,該模型也能進一步判斷序列的改變是否會影響轉錄因子的親和力,而導致某些基因表現產生變化。
生機系進一步表示,目前團隊正在開發一套能夠預測非編碼區致病變異的工具,期望能在眾多的良性變異當中,找出關鍵的致病變異,以期未來能輔助醫師尋找與特定疾病相關聯的變異,協助精準診斷。
.png)
圖:利用CNN建立轉錄因子偏好結合之DNA序列特徵模型架構圖。
The Department of Biomechatronics Engineering developed a framework diagram of the DNA sequence feature model of transcription factor preference binding using a convolutional neural network (CNN), as shown in the Figure. The research group led by Prof. Chien-Yu Chen has established a deep learning model for predicting the binding sites of transcription factors in a K562 cell line using CNN. This deep learning model uses the concepts and advantages of CNN for image learning to transform a one-dimensional sequence into a two-dimensional array that is similar to an image for learning. The developed model can achieve an average prediction accuracy of 83.3%. The research team of Prof. Chen is currently developing a set of tools that can predict pathogenic variants in non-coding regions. It is expected that key pathogenic variants could be identified among various benign variants, thereby assisting physicians in finding variants associated with specific diseases in the future, and thus assist precision diagnoses.
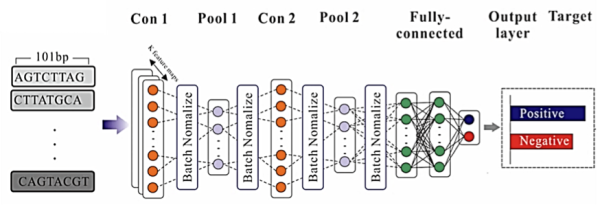
Figure. Establishment of a framework diagram of the DNA sequence feature model of transcription factor preference binding using convolutional neural network (CNN)